Pain is the most common symptom of knee osteoarthritis and often the first sign that something is wrong. Initially, the pain may occur only after physical activity, such as walking or climbing stairs. As the condition progresses, pain may become more persistent, even occurring during rest. The pain is typically described as a dull, aching sensation that worsens over time, particularly with prolonged activity or weight-bearing movements. Some individuals also experience sharp or stabbing pain during movement.
Stiffness in the knee joint is another hallmark symptom of osteoarthritis. Many patients notice that their knee feels particularly stiff after periods of inactivity, such as upon waking in the morning or after sitting for an extended time. This stiffness usually improves with gentle movement but may return after strenuous activity. As osteoarthritis advances, stiffness can become more persistent, making it difficult to fully extend or bend the knee.
Swelling around the knee joint is a common symptom caused by inflammation and excess fluid accumulation. This occurs when the joint tissues become irritated due to cartilage breakdown. Swelling may vary in severity, sometimes presenting as mild puffiness and at other times as significant joint enlargement. The skin around the knee may also appear red and feel warm to the touch, particularly during flare-ups of inflammation.
Cracking or Popping Sounds (Crepitus)
Many individuals with knee osteoarthritis report hearing or feeling grinding, popping, or cracking sounds when moving the knee. This phenomenon, known as crepitus, results from roughened cartilage surfaces rubbing against each other. While occasional popping sounds can be normal, frequent or painful crepitus may indicate worsening joint damage. In some cases, loose fragments of cartilage or bone can contribute to these noises and sensations.
As knee osteoarthritis progresses, individuals may experience a gradual decline in their ability to move the joint freely. Bending and straightening the knee can become more difficult, affecting daily activities such as walking, sitting, or getting in and out of a car. In severe cases, the knee may feel “locked” or resistant to movement, further limiting function and mobility.
Knee Osteoarthritis Pain Relief in Los Angeles
Muscle weakness and joint instability often develop as osteoarthritis advances. The weakening of surrounding muscles, particularly the quadriceps, can make it harder to support the knee properly. Patients may feel as if their knee is “giving out,” leading to an increased risk of falls. This instability can make standing for long periods or engaging in weight-bearing activities more challenging.
In response to cartilage loss, the body may develop small bony growths called osteophytes or bone spurs. These can form around the knee joint, leading to increased stiffness and discomfort. In some cases, bone spurs can press on surrounding tissues or nerves, contributing to additional pain and mobility issues.
Changes in Gait & Posture
Due to pain, stiffness, and instability, many individuals with knee osteoarthritis unconsciously alter the way they walk. Affected individuals may shift their weight to the opposite leg or develop a limp to reduce discomfort. Over time, these changes in gait and posture can lead to secondary problems, including hip, lower back, or ankle pain due to altered biomechanics.
Increased Sensitivity to Weather Changes
Many people with knee osteoarthritis report that their symptoms worsen with changes in weather, particularly in cold or damp conditions. Although the exact reason for this phenomenon is not fully understood, it may be related to changes in barometric pressure affecting joint tissues. Some individuals notice increased stiffness, swelling, or pain during seasonal shifts or rainy days.
Fatigue & Emotional Impact
Living with chronic knee osteoarthritis can be physically and emotionally draining. Persistent pain and mobility challenges can contribute to fatigue, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks. Additionally, the limitations imposed by knee osteoarthritis may lead to frustration, anxiety, or depression, especially if the condition significantly impacts independence and lifestyle.
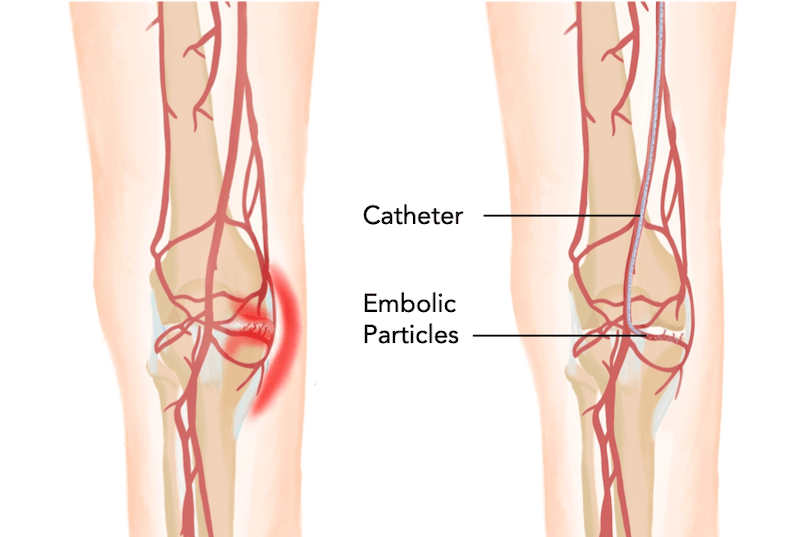
Genicular Artery Embolization in Los Angeles
Are you living with osteoarthritis symptoms? Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are treatments that can help alleviate your symptoms and improve your mobility, including:
- Physical therapy and low-impact exercises
- Pain management with medications or injections
- Weight management to reduce stress on the joints
- Supportive devices like braces or orthotics
- Genicular artery embolization to relieve knee pain
- Surgical options such as knee replacement
At ProVascularMD, we specialize in minimally invasive genicular artery embolization (GAE). Genicular artery embolization offers a new way to treat persistent knee osteoarthritis pain without major knee surgery. Get in touch with us at ProVascularMD to learn more!